
New @GEOTECUJI paper out in @IEEEIoT
We are pleased to announce that GEOTEC members have published a new scientific article in the prestigious IEEE Internet of Things Journal. This paper is titled “Hypnos: A Hardware and Software Toolkit for Energy-Aware Sensing in Low-Cost IoT Nodes” and is part of an ongoing line of research focused on Internet of Things nodes ( IoT) and energy saving algorithms.
The work led by Alberto González-Pérez and Sven Casteleyn is transversal to the past and recent contributions of GEPTEC related to the field of IoT. It introduces Hypnos, a suite of hardware and software tools that aims to bring energy awareness to new and existing IoT nodes, allowing them to self-regulate their duty cycle considering available and consumed energy. Hypnos is fully configurable to allow developers to specify conservative or more aggressive power usage (or energy saving, depending on the perspective) strategies, balancing certainty in terms of uptime against higher sensing rates. The toolkit uses widely used hardware and software standards, providing seamless integration with the vast majority of IoT nodes. Next figure illustrates the Hypnos’ architecture.

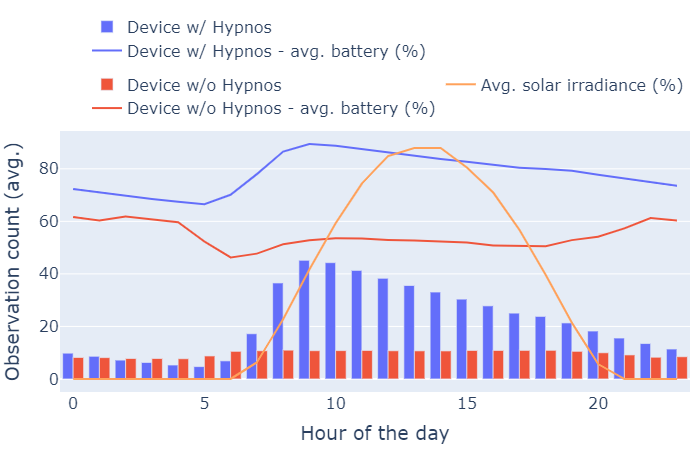
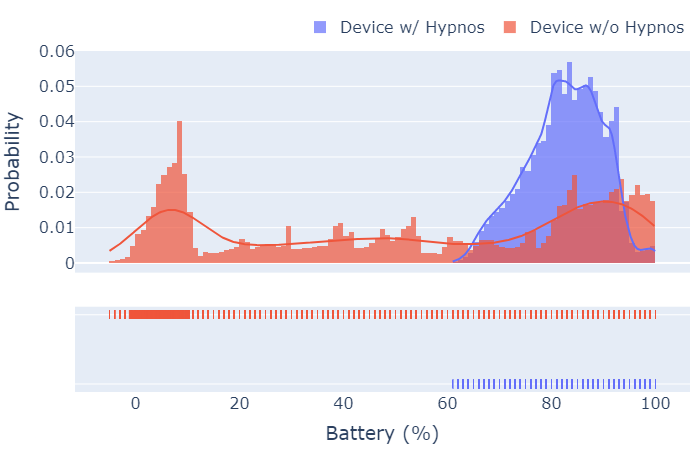
Empirical results obtained show that Hypnos, with a basic, conservative energy management strategy, is able to keep the battery of an IoT node in a safe range (60% – 80%), while delivering up to 2.25x more performance (duty cycles) by using the harvested and available energy opportunistically, in comparison with a node running with a traditional (fixed interval) scheduling strategy.
Want to learn more about Hypnos and the experiments conducted with it? Do no hesitate to contact Alberto.
The abstract of the paper appears below.
Through the Internet of Things, autonomous sensing devices can be deployed to regularly capture environmental and other sensor measurements for a variety of usage scenarios. However, for the market segment of stand-alone, self-sustaining small IoT nodes, long term deployment remains problematic due to the energy-constrained nature of these devices, requiring frequent maintenance. This article introduces Hypnos, an open hardware and software toolkit that aims to balance energy intake and usage through adaptive sensing rate for low-cost Internet-connected IoT nodes. We describe the hardware architecture of the IoT node, an open hardware board based on the Arduino Uno form-factor packing the energy measurement circuitry, and the associated open source software library, that interfaces with the sensing node’s microcontroller and provides access to the low-level energy measurements. Hypnos comes equipped with a built-in, configurable, modified sigmoid function to regulate duty cycle frequency based on energy intake and usage, yet developers may also plug in their custom duty/sleep balancing function. An experiment was set up, whereby two identical boards ran for two months: one with the Hypnos software framework and built-in energy balancing function to regulate sensing rate and the other with fixed sensing rate. The experiment showed that Hypnos is able to successfully balance energy usage and sensing frequency within configurable energy ranges. Hereby, it increases reliability by avoiding complete shutdown, while at the same time optimizing performance in terms of average amount of sensor measurements.
Cite it as:
A. González-Pérez and S. Casteleyn, “Hypnos: a Hardware and Software Toolkit for Energy-Aware Sensing in Low-Cost IoT Nodes,” in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3145338.
- Posted by geoadmin
- On 28 March, 2022
- 0 Comments




0 Comments